Fact Sheet – Everything You Should Know
In this Oxaliplatin fact sheet, you’ll get to know about the precautions, usage, possible side effects, and the types of cancer that you can treat with this chemo drug.
Embed this Infographic on your site:
<a href='https://dr-adem.com/oxaliplatin-fact-sheet/'><img src='https://dr-adem.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Oxaliplatin2-scaled.jpg' alt='Oxaliplatin Fact Sheet'/></a>Here’s the Oxaliplatin fact sheet to get detailed information about Oxaliplatin
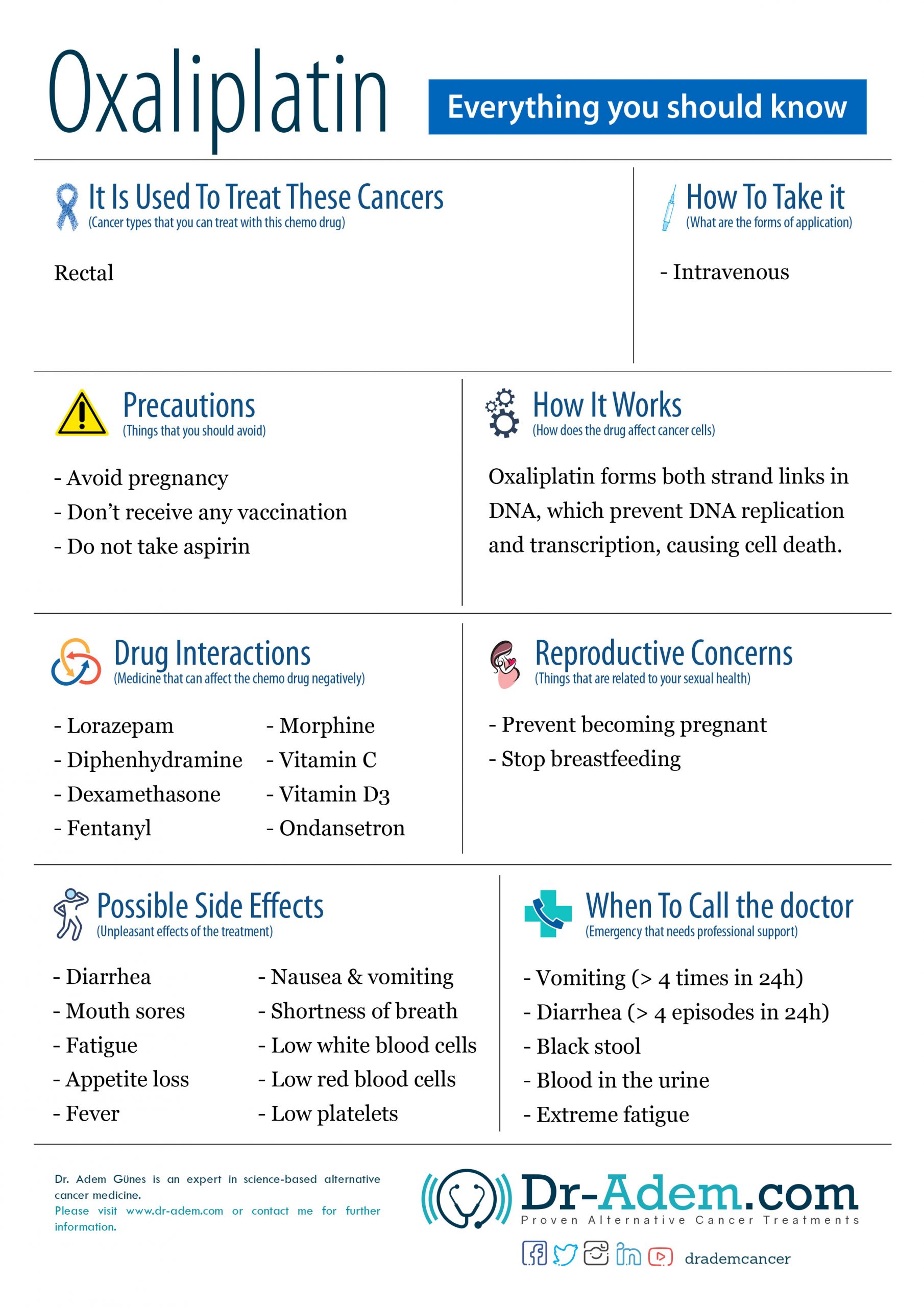
It Is Used To Treat These Cancers
(Cancer types that you can treat with this chemo drug)
- Rectum
- Colon
How To Take it
(What are the forms of application)
- Intravenous
Precautions
(Things that you should avoid)
- Avoid pregnancy
- Don’t receive any vaccination
- Do not take aspirin
Mechanism of Action of Oxaliplatin
(How does the drug affect cancer cells)
Oxaliplatin belongs to the alkylating agents (Platine analogs subgroup) and is a cytostatic drug (causes cellular death or inhibits its growth). It forms complexes that bind to 2 neighboring guanine bases (building blocks of the DNA strands) in the DNA, causing a stop into its replication, which results in the disruption of cellular metabolism.
Drug Interactions
(Medicine that can affect the chemo drug negatively)
- Lorazepam
- Diphenhydramine
- Dexamethasone
- Fentanyl
- Morphine
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D3
- Ondansetron
Reproductive Concerns
(Things that are related to your sexual health)
- Pregnancy prevention during and until 6 months after the treatment (men and women)
- Stop breastfeeding
- Consider sperm freezing if willing to bear children
Possible Side Effects
(Unpleasant effects of the treatment)
- Diarrhea
- Insomnia (difficulty sleeping)
- Fatigue
- Mouth ulcers
- Neurotoxicity (peripheric neuropathy)
- Malaise
- Conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eye mucosa; pink eye)
- Cough
- Nose bleeds
- Liver toxicity
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Nausea & vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Low white blood cells: raise the risk of bacterial infection
- Low red blood cells: can lead to fatigue, general lack of interest and drive to be active
- Low platelets: can lead to bleeding (nose, gums) and in extreme cases to internal bleeding (intestinal, brain, joints)
- Infertility
When To Call the doctor
(Emergency that needs professional support)
- Vomiting (>4 times in 24h): can lead to severe dehydration and electrolyte disbalance
- Diarrhea (>4 episodes in 24h): can also lead to severe dehydration and electrolyte disbalance
- Black stool: can be a sign of intestinal bleeding
- Blood in the urine
- Extreme fatigue: can be a sign of severe anemia (low blood cells)
- Fever > 37,8°C


