In this piece of content, you are going to know about how Magnetic resonance imaging works. So, let’s start …
An MRI is a non-invasive medical imaging test. It produces images of almost all the internal structures of the body, using a strong magnetic field.
How Magnetic Resonance Imaging Works:
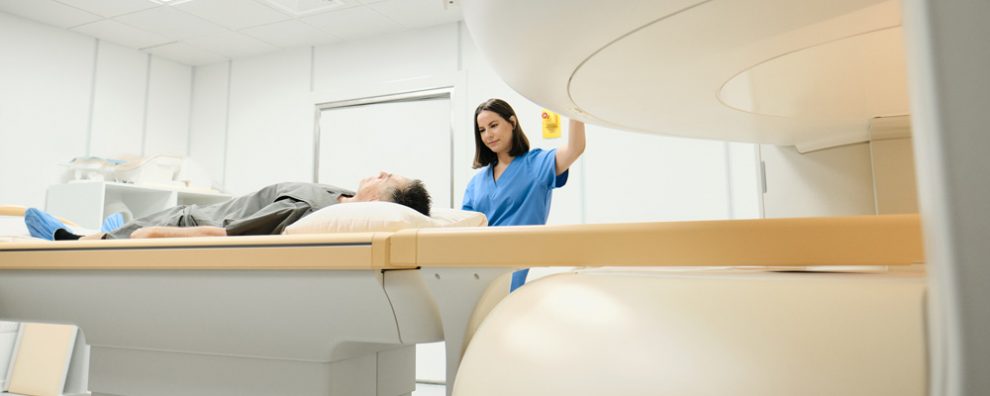
The patient lays on the examination table. Bolsters and straps are used to ensure that the patient remains still while maintaining a proper position during the exam.
If the MRI exam requires the use of contrast material, a nurse will insert an intravenous (IV) line in the vein of the patient’s arm or hand.
The whole MRI examination (preparation plus recording) may take between 15 to 45 minutes.
MRI tests are not painful. Some patients get a feeling of being closed in (claustrophobia). It is essential, therefore, to prescribe a sedative for patients who are likely to become anxious. Less than 1 in every 20 patients will need a sedative.
Imaging will take from a few seconds to several minutes. During this time, the patient should remain perfectly still.
Some recordings will require the patient to stop breathing for short periods.
The patient can ask for earplugs or headphones to block the noise of the humming and thumping sounds that occur during an MRI.
Benefits of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- An MRI is non-invasive and does not expose patients to ionizing radiation.
- As opposed to CT scanning and X-rays, which use contrast material based on iodine, MRI contrast material is less likely to generate allergic reactions.
Risks of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- The intense magnetic radiation presents no harm.
- After the injection of contrast material, there is a small risk of allergic reaction. Usually, such reactions can be easily managed with medications.
Contraindications:
The patient should make the radiologist aware of the presence of electronic or any other medical device inside the body.
- Pacemaker or internal (implanted) defibrillator
- Ear implants (implants in the ear)
- Artificial heart valves
- Drug infusion ports
- Metallic joint prostheses or artificial limbs
- Implanted nerve stimulators
- Surgical staples, metal pins, plates, screws, or stents
Limitations:
- To get high-quality images, the patient will be required to stop breathing and maintain a still position during a short period.
- For some people, the MRI tunnel might be very tight, causing discomfort during the procedure
- When compared with other imaging methods, MRI scanning is more expensive and takes longer to perform.
Conclusion:
Tumor MRI is one of the best imaging techniques in this modern era. It is a non-invasive medical imaging test to identify various structures of the body. It has no side effects and causes no harm to the body as magnetic radiations are harmless.
Source:
1.Magnetic Resonance Imaging. http://www.medicinenet.com/mri_scan/page2.htm. Accessed 9/16/16.
2. http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=bodymr
3. http://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/magnetic-resonance-imaging-mri